Algorithmic Game Theory: Its Importance, Apps, and Business Strategies
What Is Game Theory?
Game theory is defined as the study of strategically interdependent behavior among rational and self-interested agents. Strategic interdependence refers to the outcome of a participant's choice of action which is dependent on the actions of other participants.
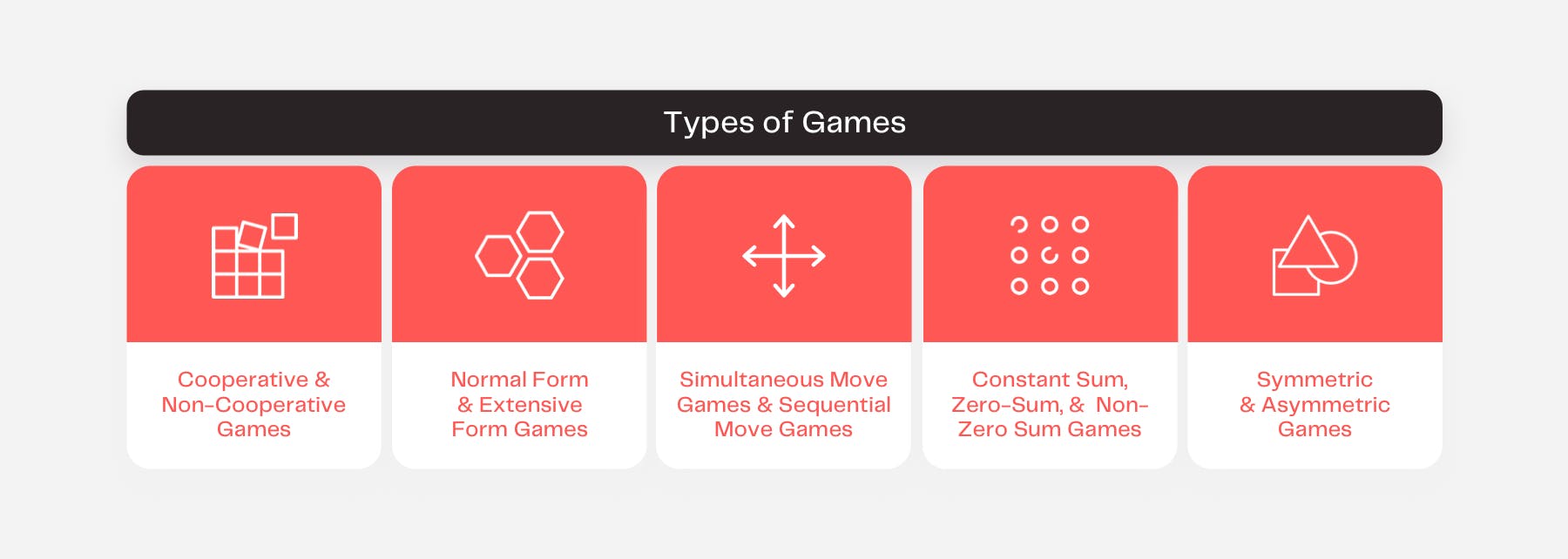
Game Theory: Game Types
Originally, the concept of game theory addressed zero-sum games which describes a situation where each participant's gains or losses are exactly balanced by those of the other participants. This indicates a highly competitive environment where, if in the case of only two players, player one’s win would result in player two’s loss. However, as the theory evolved in the 21st century, the concept now applies to a wide range of behavioral interactions and is considered a superordinate for the science of logical decision-making in humans and computers.
Different types of games help in the analysis of different types of problems and are formed on the basis of the number of players involved in a game, symmetry of the game, and cooperation among players.
Game Theory in Action: A Use Case Example
The prisoner’s dilemma is debatably the most well-known example of game theory and it remains the most popular example to illustrate the concept of game theory in a real-life scenario.
In the case of the prisoner’s dilemma, let’s say that two guilty prisoners have been arrested for shoplifting. Each prisoner is kept in a completely isolated prison cell. This means that each prisoner cannot see or communicate with the other.
A police officer then individually offers each prisoner a deal with the following terms:
- If Prisoner A confesses and agrees to testify against prisoner B, who does not confess, the charges against Prisoner A will be dropped and they are free to go.
- If Prisoner A does not confess but Prisoner B does, Prisoner A will be convicted and the prosecution will seek the maximum sentence of 10 years.
- If Prisoner A and Prisoner B both confess, both prisoners will be sentenced to five years in prison.
- If neither Prisoner A nor Prisoner B confesses, both prisoners will be charged with misdemeanors and will be sentenced to one year in prison.
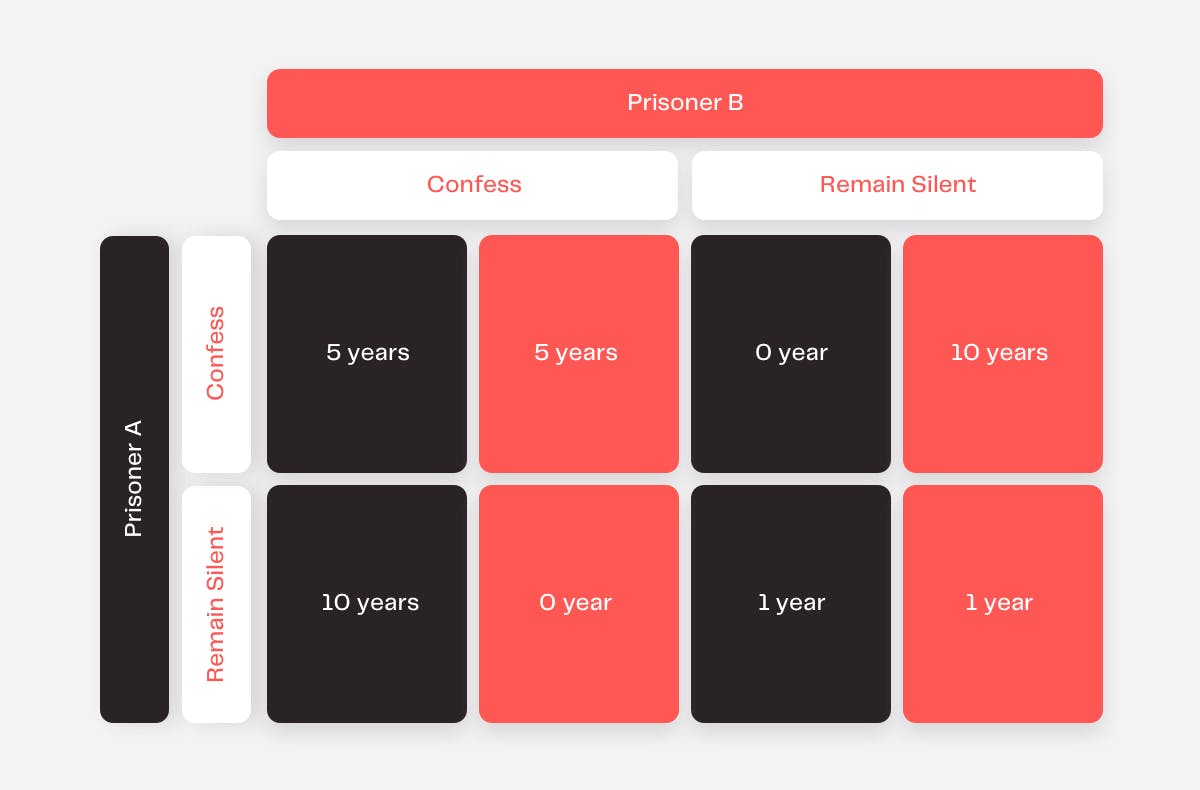
It appears the situation in which the two prisoners cooperate and do not confess is a clear optimal strategy. However, since each prisoner is held separately, they would not know the other prisoner’s decision until they had made their own. Blindly trusting the other prisoner with the possibility of getting 1,5, or 10 years in prison suddenly becomes a high-risk situation.
The implications of the prisoner’s dilemma indicate when each individual pursues their own self-interest, the outcome is worse than if they had both cooperated. This dilemma, where the incentive to remain silent (cooperate) or to confess (defect) plays out in numerous ways in business.
Game Theory: Real-World Applications in Business
From a business perspective, game theory encourages an organization to consider a competitor’s likely moves and the implications of these moves for the development of its own strategy. This enables the organization in question to 1) Get into the mind of competitors and; 2) Think forward and reason backward.
Game theory is useful in analyzing and understanding a number of situations that take place in the business world. A classic example of this is when two competitors contend for market share.
Let’s look at an example of two competing organizations, Samsung and Apple, that are considering strategies for expanding market share. Let’s assume that Samsung is considering reducing the price of its smartphones. If Samsung goes ahead with this plan, Apple may have no choice but to follow suit to retain its share of the market. However, this may result in a significant drop in profits for both companies.
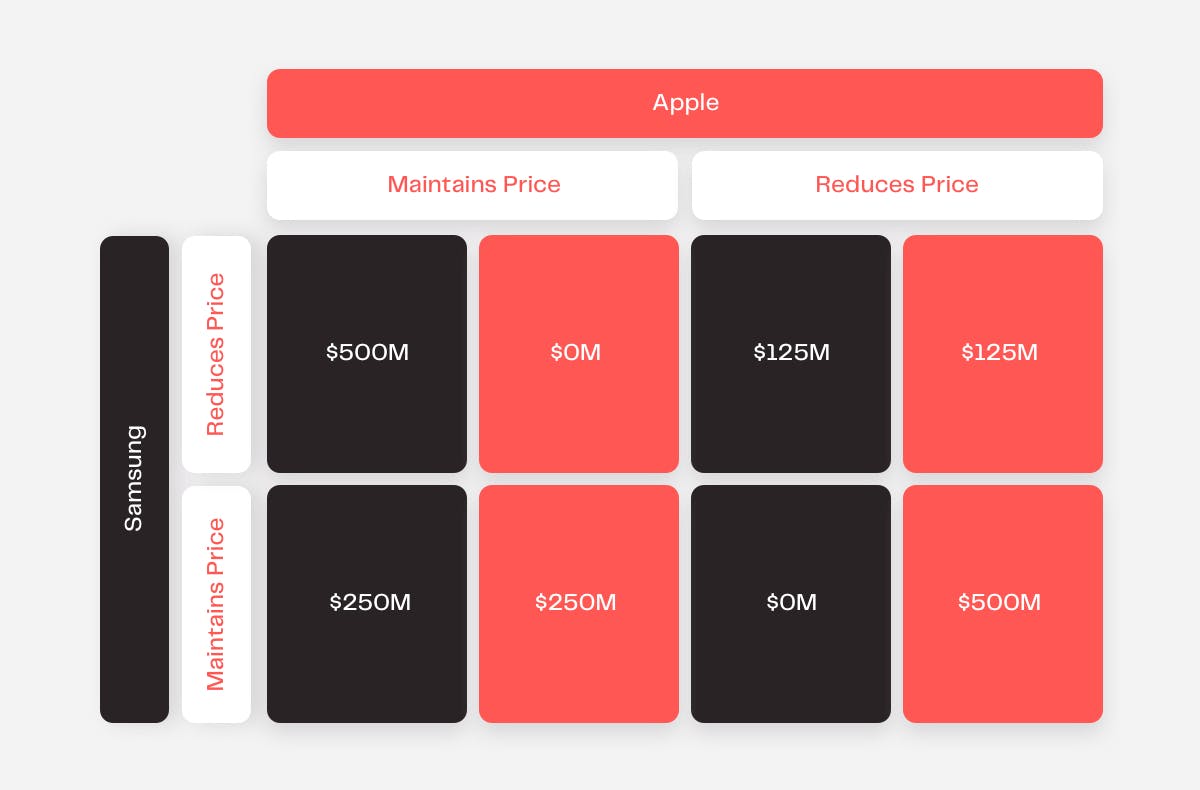
- If both Samsung and Apple maintain current prices, profits for each company increase by $250 million as a result of normal growth in demand.
- If Samsung reduces prices and Apple does not, profits increase by $500 million for the former because of greater market share due to a higher sales volume.
- If both Samsung and Apple reduce prices, the increase in smartphone purchases offsets the lower pricing structure and each organization’s profits increase by $125 million.
To better understand the implications of game theory applied to the real world, three additional business scenarios are presented below:
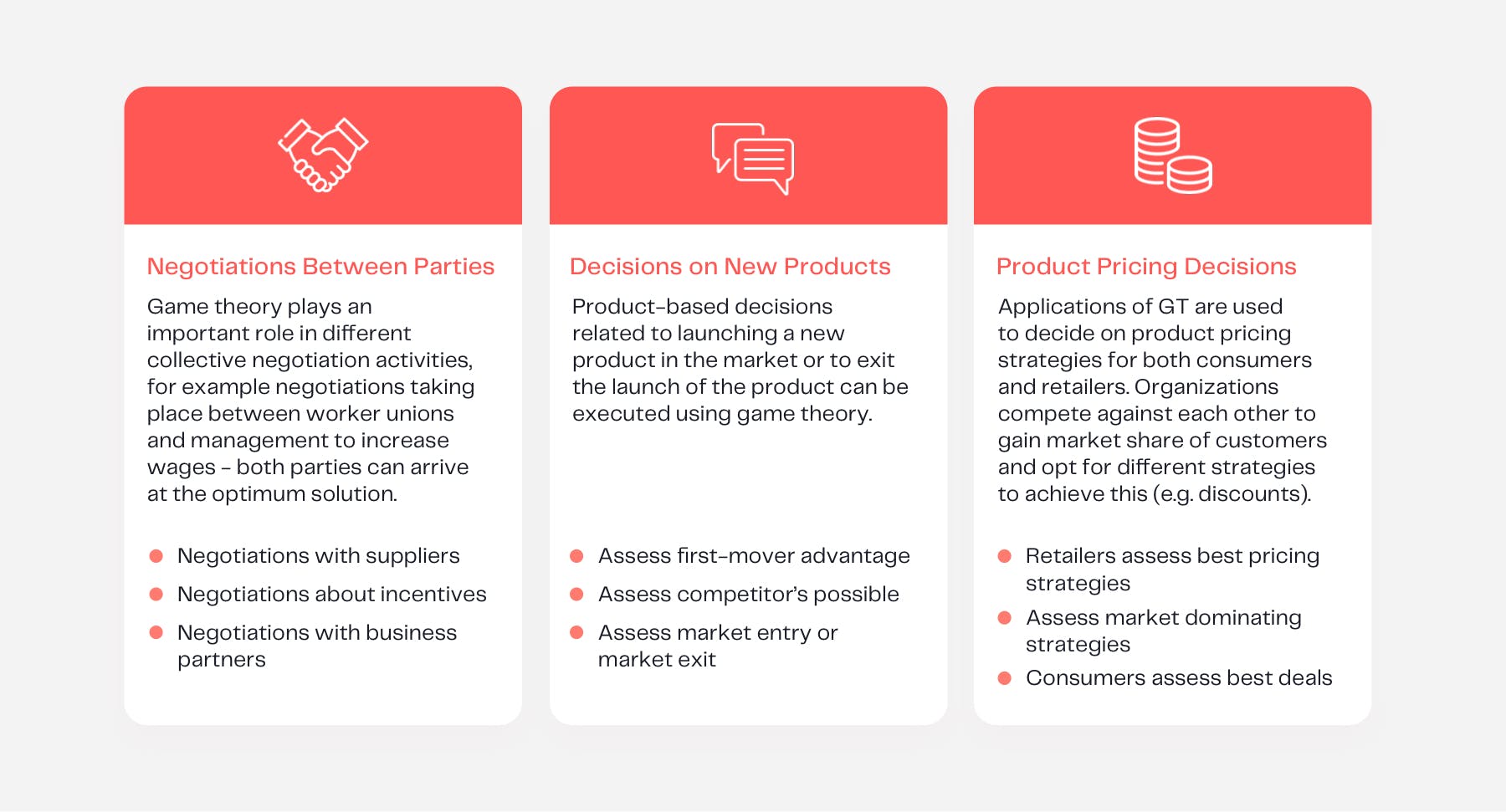
Some businesses apply counterintuitive strategies to deter competitors from analyzing their strategy and will even explore additional strategies at how to minimize their maximum loss if they were to come off second best in any given situation.
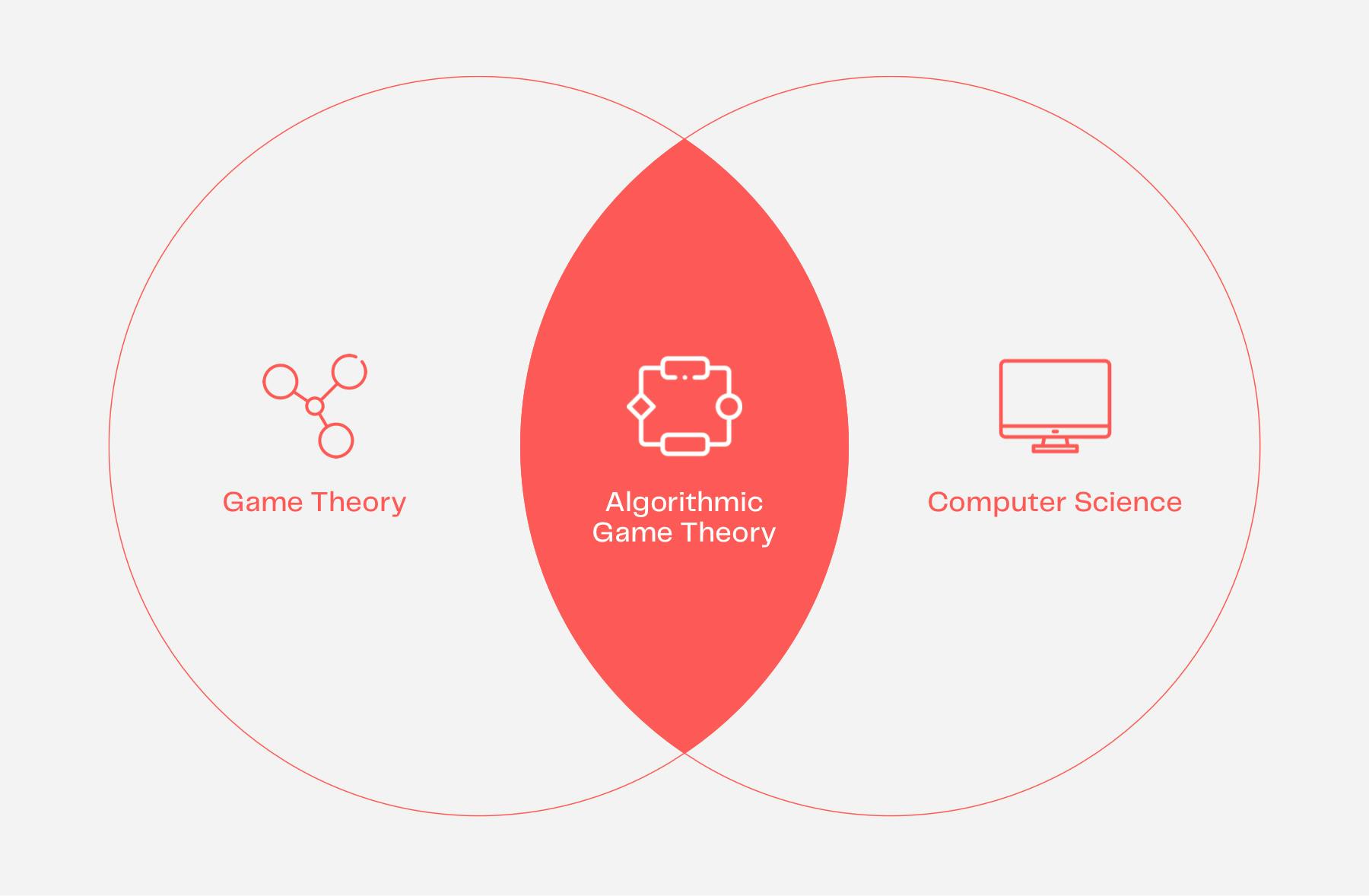
Algorithmic Game Theory
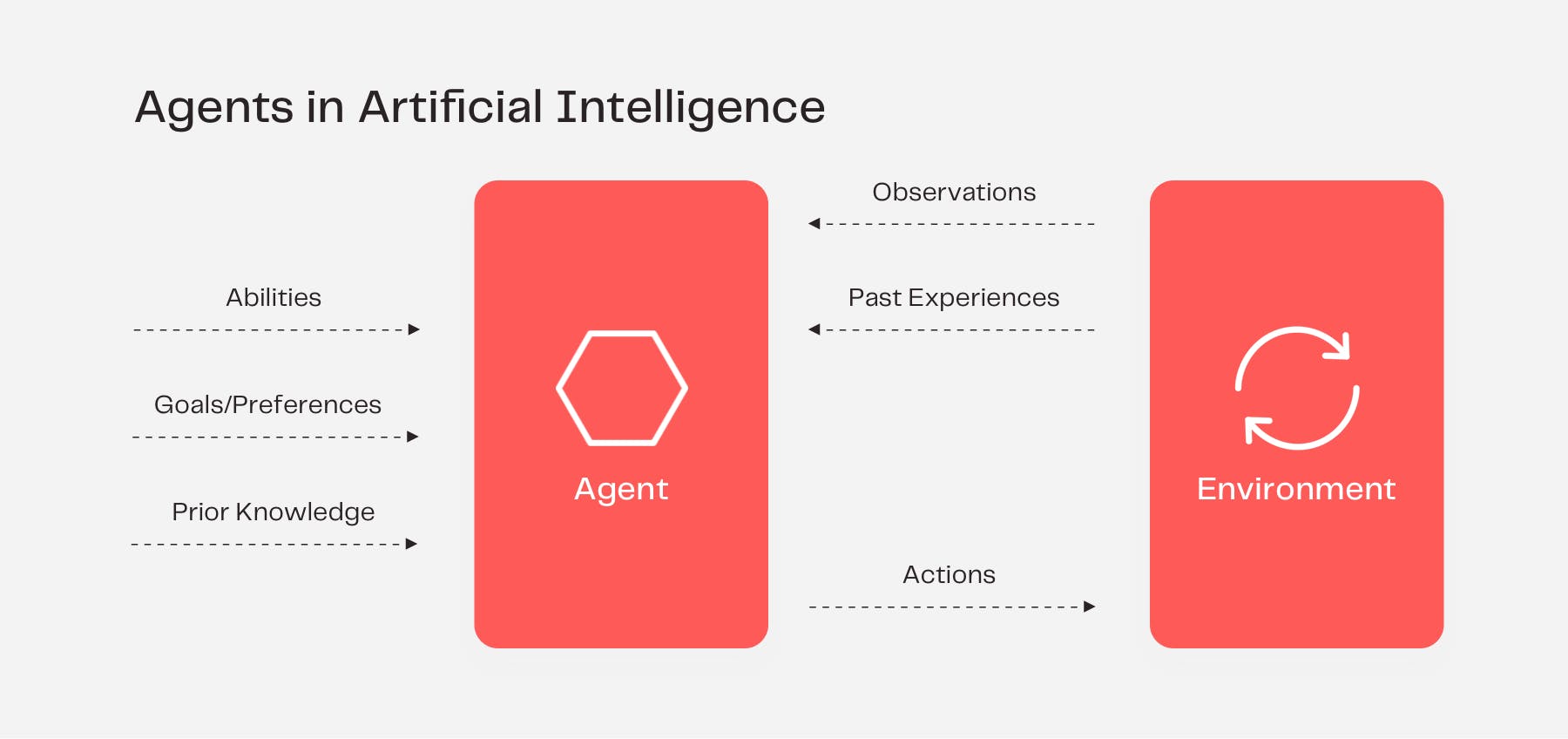
Today, game theory is a crucial element in building AI and machine learning models. These AI systems are characterized by the connection between a rational agent and its environment. Agents perceive the environment through sensors, autonomously take action, and may improve their performance with learning and knowledge. As AI systems play an increasingly integral role in business, it’s important to understand how different systems will interact with one another.
A number of use cases exist where these intelligence agents play a significant role in business. Some autonomous intelligent agents are designed to function in the absence of human intervention. For example, software agents can be applied as automated online assistants where they function to perceive the needs of customers to perform personalized customer service.
Algorithmic game theory is at the intersection of game theory and computer science, with the objective of understanding and designing algorithms in strategic environments. These algorithms are designed with the end objective (output) in mind. When applied to a business case, these algorithms are designed with incentives (typically some sort of economic benefit) so that participants (rational agents) act optimally as previously defined by the organization in their business strategy. Likewise, it is naturally assumed that none of the players in the market will diverge (defect) from the strategy identified by the algorithm because there is no incentive to do so.
Multi-agent systems are the most prominent application of algorithmic game theory. Multi-agent environments comprise more than one agent or system, for example, autonomous robots cooperating in Amazon’s warehouses.
The game theory facilitates important capabilities that multi-agent systems require to enable different AI programs to interact in order to reach a goal. These systems arise frequently with software service providers or in modern computer networks. For example, digital advertisers want to place their ads as prominently as possible while paying as little as possible.
The business model of many organizations relies on trade and marketing in computational markets on the internet.
The Benefits of Algorithmic Game Theory in Business Operations
As the corporate landscape and needs of consumers become more complex, business leaders are focusing their efforts on developing efficient algorithms for optimization in economic environments.
Algorithmic game theory offers an approach for organizations to: 1) model strategies and; 2) leverage mathematical tools for data analysis. While each organization may employ a different algorithm, the benefits that each organization stands to reap from its application include:
Reducing Business Risk
Risk analysis makes use of game theory in determining optimal price strategy, expected market shares, expected income, and the number of customers. All of this information is compared to the current performance of the organization in question, the market, the competitive landscape, and the technologies in use.
Obtaining Insights About Competitors
Game theory is effective in sourcing information on various aspects that relate to the competitiveness of the business such as its strategies, strengths, and weaknesses. This enables an organization to increase the value of its strategy and value proposition based on competitive insights.
Improving Internal Decision-Making Processes
By simulating various business scenarios, organizations become more efficient in their decision-making techniques. Even if organizations act rationally and follow their own self-interest, the best outcome is difficult to secure when they don’t cooperate with other players in the market. Often, the best strategy is to continually scan the market for potential alliances so that organizations can cooperate to some degree to become part of oligopolies and dominate the market.
Performing Large-Scale Data Analysis
Large datasets can be analyzed computationally to reveal patterns, trends, and associations — particularly human behavior and interactions. Organizations can use big data analytics systems and software to make data-driven decisions that improve business-related outcomes such as more effective marketing, customer personalization, and improved operations.
The use of algorithmic game theory is fundamental in helping organizations better understand and control multi-agent systems in today’s increasingly complex world.
Ultimately, organizations are leveraging game-theoretic frameworks to think more clearly about what other market players might do in cooperative and competitive situations. Game theory yields useful insights that aren’t always apparent from decision analysis alone, leading to the creation of valuable new alternatives.




