How Digitization Can Provide A More Sustainable Future

The Digital Revolution and Its Role in the Climate Revolution
Since the dawn of industrialization, it has been about growth through innovation. But it is the achievements of the first three great industrial revolutions that have brought us to where we are today: amid climate change.
In addition to increased progress and prosperity, the technologies have also laid the foundation for increased CO2 emissions. This started with the steam engine and continued with the invention of electricity. Its increased energy demand initially came from renewable sources such as wind and water power but was then increasingly met by the use of fossil fuels. The third industrial revolution finally brought with it the establishment of the internet - and with it the increasing number of data centers that are extremely energy-hungry.
· Around 2.7% of Europe's electricity demand is accounted for by such data centers
· As early as 2030, the figure is expected to be 3.2 percent
· The energy demand of the users' devices comes on top of that
In a world where for a long time there seemed to be no limits, we are now being made aware of the finite nature of our planet and, with it, of our lives.
But now we are in the middle of the fourth Industrial Revolution. And of all things, it can become a game-changer. Whereas industrialization used to be the driving force behind innovative developments and the shaping of a new world, today it is digitalization. It has what it takes to make industrialization more efficient and sustainable.
The Impact of IoT and AI on the UN's Sustainability Goals
Only through digital innovations will we manage to produce, consume and thus live more sustainably. In Germany for example, the entire internet infrastructure consumes about 55 TWh of energy per year and generates as much CO2 as the annual domestic air traffic. If IT applications were intelligently networked, this could make a major ecological contribution. In Germany alone, up to 190 million tonnes of CO2 could be saved annually, according to the German government.
Probably the most revolutionary digital networking is the Internet of Things (IoT). In its report "State of the Connected World", the World Economic Forum (WEF), together with the Global Internet of Things Council and PwC, examines the impact of the IoT on society and the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals.
The result:
· IoT's business benefits will be supplemented and enhanced through its impact on our environment and society as a whole
· An analysis of more than 640 IoT deployments showed that 84% of existing IoT deployments address or have the power to advance the SDGs
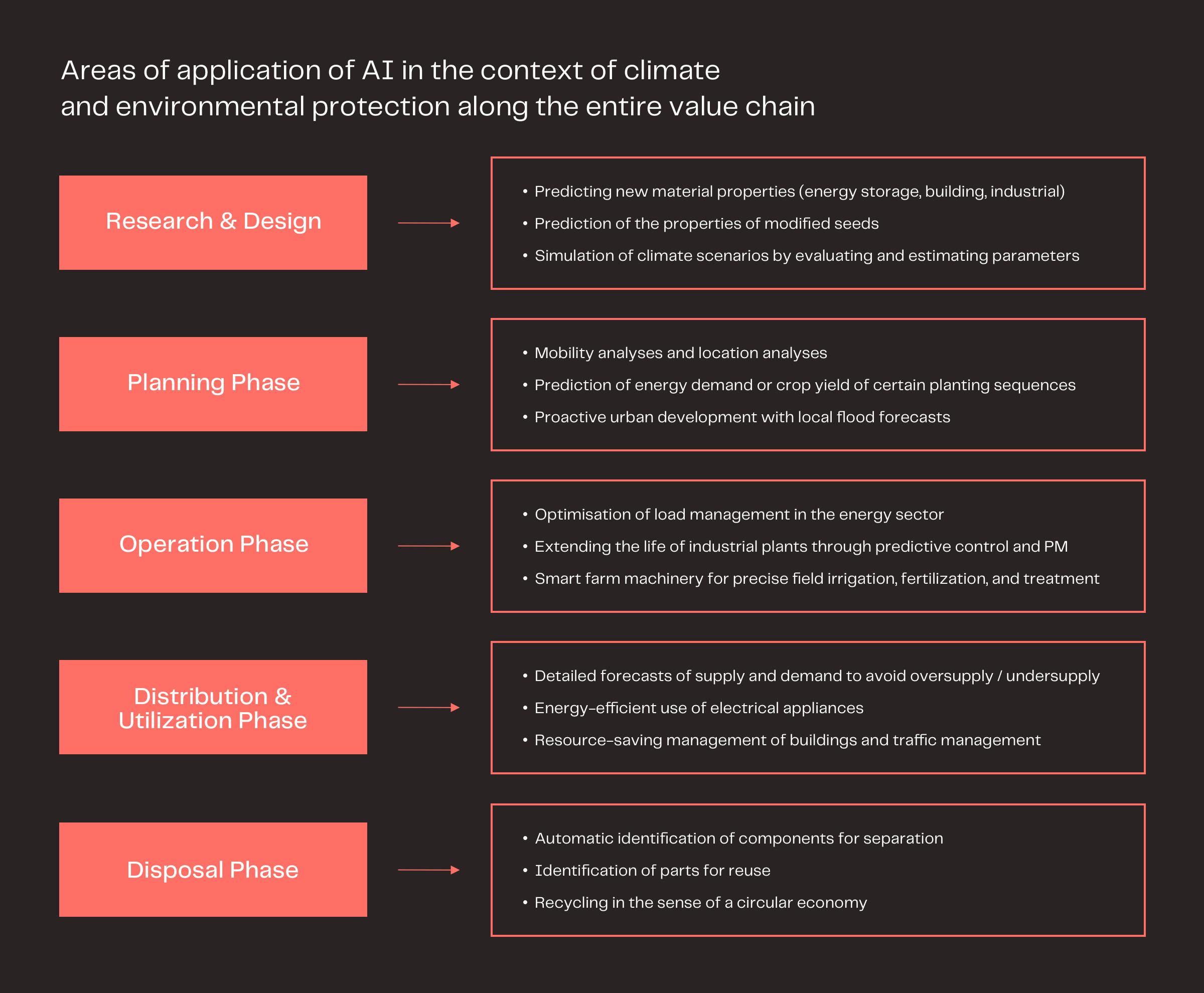
· Artificial intelligence (AI) can also be used in numerous economic sectors and situations to help address environmental impacts and climate change
· AI comes in at 82% in terms of its potential to positively impact the SDGs

Digitalization can combat climate change sustainably and across sectors
AI also has an enormous potential to decouple economic growth from rising carbon emissions.
According to estimates from the study "How AI can Enable a Sustainable Future", AI use for environmental protection could contribute up to US$5.2 trillion to the global economy by 2030. This would be an increase of 4.4 percent over the expected economic development.
In parallel, the application of AI levers could reduce global greenhouse gas emissions by 4 percent by 2030. That would be a total of 2.4 gigatonnes of CO2 emissions - an amount equal to the total expected emissions of Australia, Canada, and Japan in 2030.
The areas of application are broad and range from energy, agriculture, and mobility to cross-sectoral topics such as raw material and material efficiency, energy efficiency, and waste management. "Even though IoT might not be the whole or the only solution, I believe it can be the catalyst of a greener digital transformation that puts both sustainability and profitability at the core of a business operating model. A model built not just on productivity, but on efficiency," says Erik Brenneis, director of IoT at Vodafone Business.

How IoT and AI are shaping the Machine Economy
The link between digitalization and the physical world is characterized by technologies that could revolutionize entire industries on their own. Take blockchain technology, the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and artificial intelligence (AI), for example.
IoT solutions have the advantage of enabling communication between assets and people. If the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are linked, it becomes possible, for example, for companies to better understand their environment because they can collect and analyze large amounts of useful data. This will make completely automated business models possible: a Machine Economy in which machines, plants, logistics and production communicate autonomously with each other and carry out transactions.
In the future, networked machines will lease themselves, hire maintenance technicians or pay for spare parts. This networking will not only optimize individual production steps, but the entire value chain with all phases of the product life cycle. The Machine Economy will therefore make us more productive. This benefits the economy and the environment in equal measure.
Take the innovation of Predictive Maintenance - a prime example of more sustainability, cost savings and safety. The permanent, automated monitoring of machines avoids unexpected or unnecessary down times and thus precious energy that is needed to run the equipment.
For machine manufacturers, this also results in new business areas such as Machine Resource Management from Makula, which also enables SMEs to manage all machines efficiently from one place.
What are the driving forces and counterforces of the Machine Economy?
Read more here.
Green Logistics: Processes become more transparent and sustainable through greater efficiency
Green logistics is a rapidly evolving field that aims to make supply chains more environmentally friendly and sustainable. One of the key ways this is being achieved is through the implementation of advanced technologies.
Technologies such as artificial intelligence, cloud-connected IoT sensors, and smart tracking and tracing systems are playing a crucial role in improving the efficiency of logistics processes. For example, these technologies enable route optimization by constantly analyzing real-time data. In the case of traffic jams or other disruptions, alternative routes can be quickly identified and selected, minimizing delays and reducing fuel consumption.
Furthermore, artificial intelligence algorithms are continuously learning and improving, ensuring that the best possible route is always chosen based on current conditions. This not only leads to significant reductions in emissions but also enhances transparency and visibility throughout the entire supply chain.
By leveraging these technological advancements, companies can not only streamline their operations but also contribute to creating a greener future. The ability to monitor and track shipments in real-time allows for better inventory management, minimizing waste and preventing overproduction. It also enables proactive measures to be taken in case of unexpected events or emergencies, reducing the risk of delays or disruptions.
In addition to these environmental benefits, green logistics also presents opportunities for cost savings. By optimizing routes and reducing fuel consumption, companies will lower their transportation costs while simultaneously lowering their carbon footprint. Moreover, implementing sustainable practices can enhance a company’s brand image, attracting environmentally conscious customers who value ethical business practices.
Overall, green logistics represents a paradigm shift in how we approach supply chain management. By harnessing the power of cutting-edge technologies and prioritizing sustainability goals, businesses can create a more transparent and efficient ecosystem that benefits both the environment and their bottom line.
Digitization of the Agriculture & Food Industries: An Underestimated Field for a Better World
Digitization and IoT are also making inroads with farmers. They need to become more efficient and productive, while also cutting costs. Challenges are the high price pressure, international competition and increasing demands on product quality. Other drivers are climate change and the need to reduce water consumption. IoT in agriculture supports farmers in overcoming these difficulties. Smart networking of equipment, machinery, fields and livestock saves unnecessary travel, costs and time.
This includes:
· Precision (Livestock) Farming
· Smart Irrigation for more efficient water use in irrigation.
· Agriculture Drones monitor seeds, crops and livestock
· Smart Greenhouses
· Farm Management Systems
However, it is not only agriculture that can contribute to greater sustainability through the use of technology, but also the food industry. After all, 30 percent of the world's food production is either not harvested at all or destroyed unconsumed. Of these 1.3 billion tonnes, more than one-tenth becomes unusable during processing, storage or transport. Food waste from restaurants accounts for an astonishing 15 percent of all food that is ultimately landfilled. This is a shame, considering that hunger still reigns in many parts of the world. Moreover, the mountains of waste are also an environmental problem. When the waste rots, it produces methane, a gas that promotes the greenhouse effect more than carbon dioxide.
To create a better future, businesses, civil society, governments and other stakeholders need to come together to help shape that future. And increasingly we need to do this not just in a single community or country, but on a global basis. Each of us has a responsibility to participate - and an important role to play. Let's do that step together.
Let's embrace the opportunities digital innovation such as IoT, AI and the Machine Economy offer us.




