Building A Decentralized Future With dApps

Since 2009, blockchain technology has worked its way from being a relatively unknown technology to a system that promises to disrupt traditional industries. Many have likened the revolutionary possibilities of blockchain technology to those of the internet, with the capacity to transform the ways in which people and businesses interact.
While there’s still some debate on whether the corporate blockchain hype is slowing, significant interest remains, with investors placing more than $23.7 billion into early-stage blockchain startups since the beginning of 2013. Perhaps even more indicative of its disruptive potential, Oracle, Amazon, Roche, Goldman Sachs, and many more established companies continue to investigate pilot projects that explore blockchain’s possibilities.
As interest in blockchain and DLT (distributed ledger technologies) continues to ebb and flow, both organizations and individuals are exploring its real-world applications. These decentralized applications, or dApps, are characterized by their distributed, resilient, and transparent nature.
Before trying to comprehend the full functionality of dApps, it’s important to be familiar with their underlying technology — blockchain. A blockchain is a digital ledger of transactions organized in ‘blocks’ that are linked together by cryptographic validations. By design, blockchains are resistant to the modification of their data and are not managed by a single entity.
Those already keeping an eye on the blockchain space will be aware of the hype surrounding dApps. While Bitcoin may have initially paved the way for cryptocurrencies, Ethereum was victorious in highlighting the true potential of blockchain technology. Ethereum made it possible for developers to build dApps with the introduction of smart contracts.
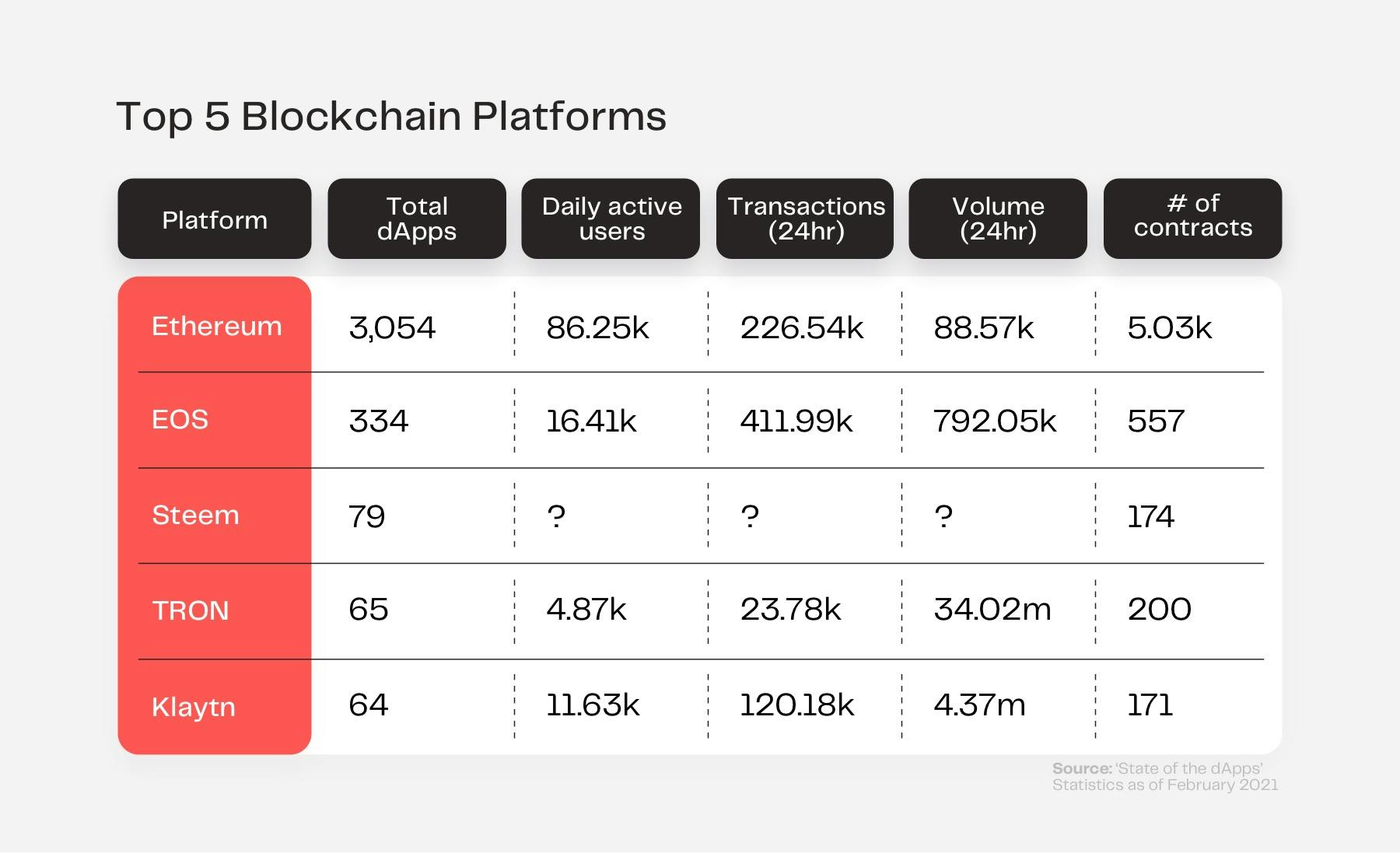
With over 3500 dApps already in existence and the total number of daily active dApp users at 138.12k and rising, some are predicting that decentralized applications will become even more common and relied upon than today’s centralized applications.
The dAppening
What is a dApp?
dApps are applications built on a decentralized network that combines backend code (smart contracts) with a frontend user interface (e.g. a website). While a frontend user interface isn’t a prerequisite for dApps, it is quite common.
To the average user, a dApp may feel like any other digital application on the web but it leverages all the benefits of its underlying blockchain protocol. While dApps can be built on a variety of different blockchain protocols and peer-to-peer systems like IPFS, Ethereum is by far the leading host of dApps.
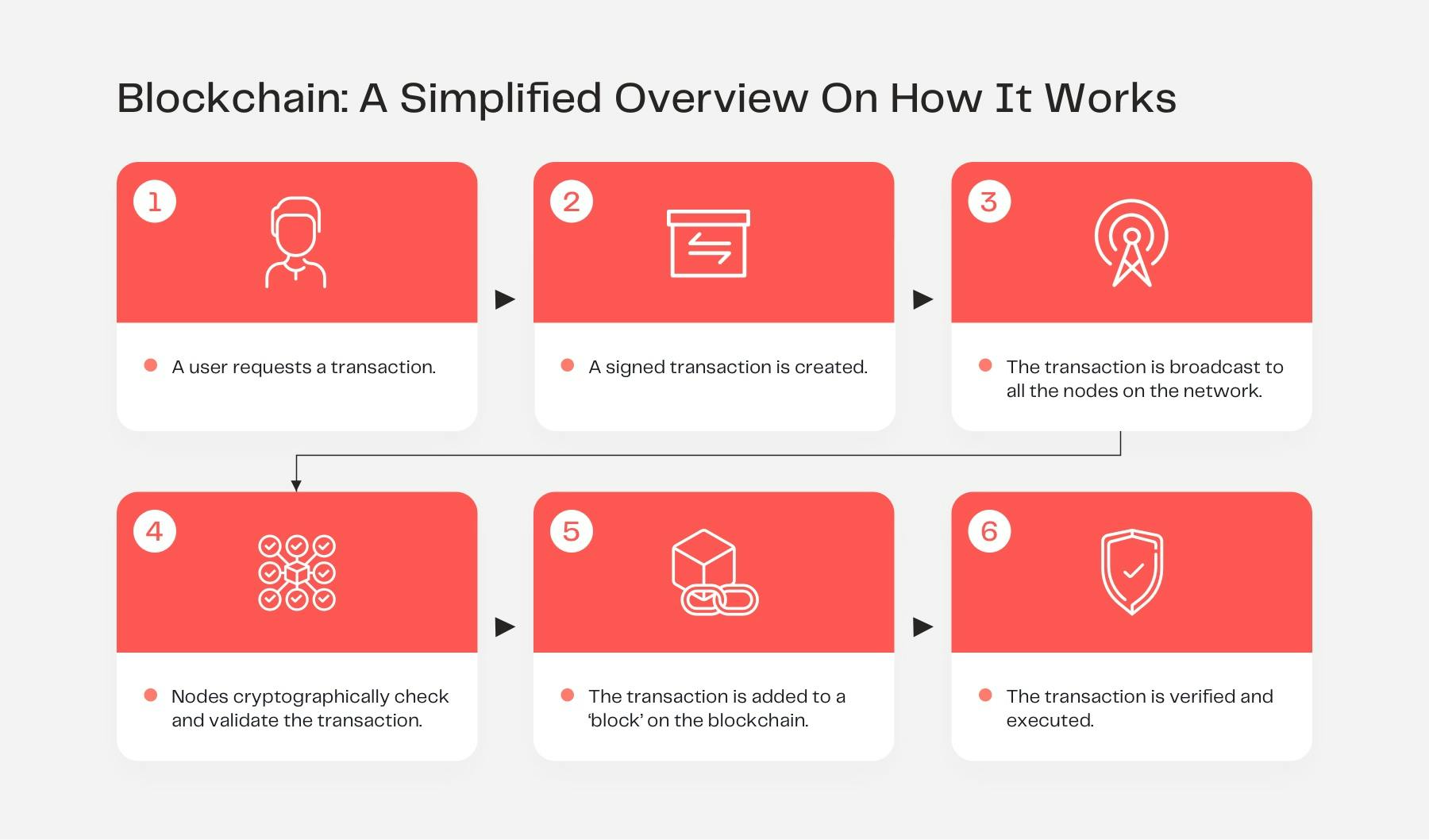
How Does a dApp Work?
In order to better understand dApp functionality, it’s important to have a basic knowledge of smart contracts. A smart contract can be thought of as a set of rules that lives on-chain and is thus visible to all network participants.
To simply illustrate the mechanics of a smart contract, let’s imagine a vending machine. If you supply the machine with the correct funds and input the right selection, you'll get the item you want. Much like a vending machine, smart contracts can hold funds that enable the programmed code to execute agreements and transactions that users request.
dApp Features
dApps differ from regular mobile and web-based apps because they aim to hand users more control over the data that these apps manage. In addition to this, dApps are:
- Often open source – Freely available and capable of modification and redistribution.
- Decentralized – Hosted on a decentralized blockchain.
- Distributed – Leverage complex cryptography as a verification method.
- Turing complete – Given the required resources, the dApp can perform any action.
- Deterministic – The same operation performed across different nodes (computers or connected devices) returns the same result.
- Isolated – If the smart contract happens to have a bug, it won’t impact the normal functioning of the blockchain network.
dApps Benefits (On Ethereum)
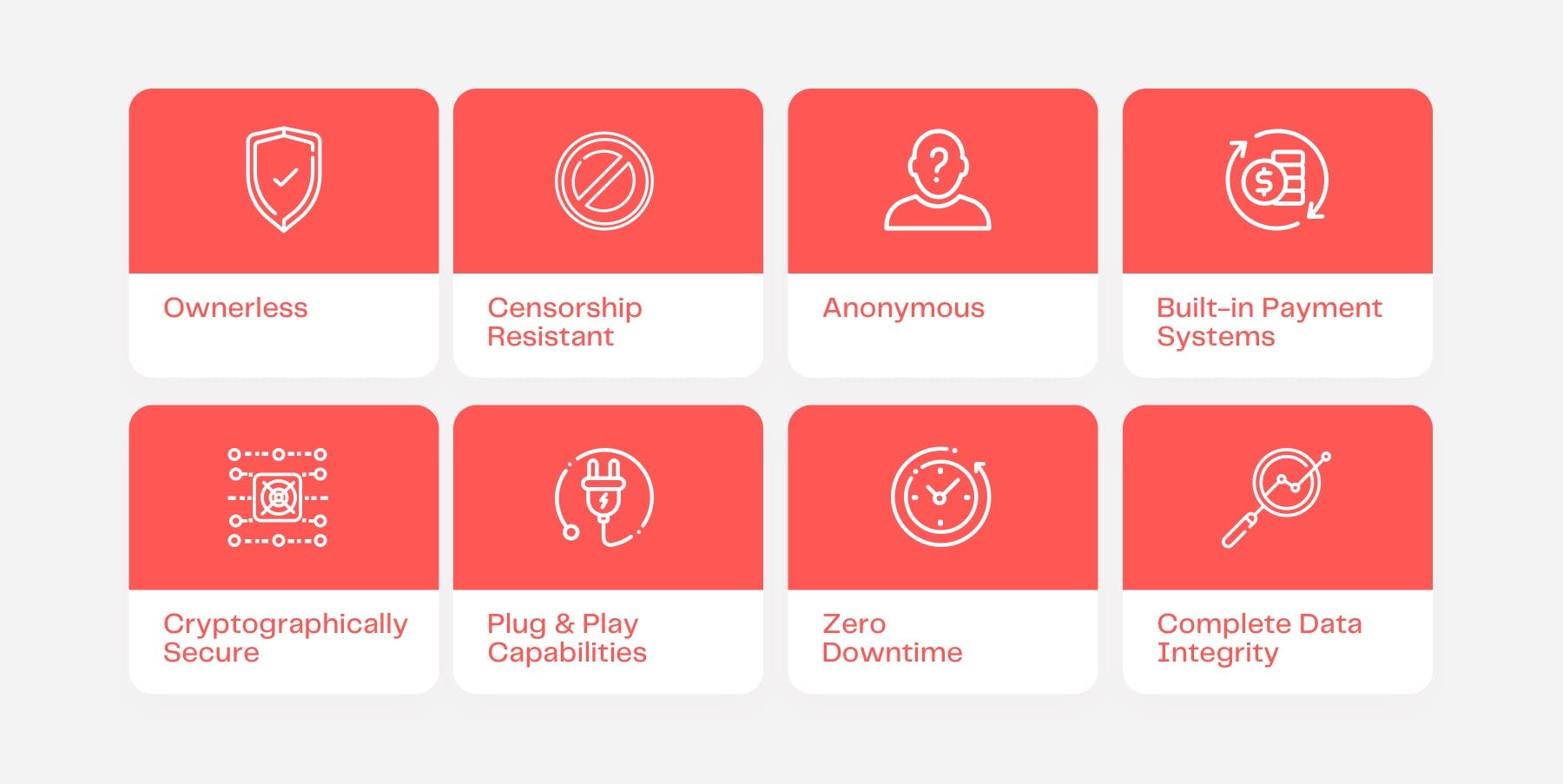
Ownerless
Once a dApp has been deployed to Ethereum, the code can’t be taken down. Anyone can use the dApp’s features even if the team or company behind the application disbanded.
Censorship resistant
No single entity on the network can prevent users from submitting transactions, deploying dApps, or reading data from the blockchain.
Anonymous
Users don't need to share their real-world identity to deploy or interact with a dApp. In most cases, users will simply need a digital wallet address.
Built-in payments
Payments are native to Ethereum via its native ETH token and several additional token standards. Developers don't need to spend time integrating with third-party payment providers.
Cryptographically secure
Cryptography ensures that attackers can't forge transactions and other dApp interactions on a user’s behalf. Smart contracts can be analyzed and are guaranteed to execute in predictable ways, without the need to trust a central authority.
Plug and play capability
dApp code is often open source and teams regularly build using other teams' work.
Zero downtime
Once the dApp is live on Ethereum, it will only go down if Ethereum itself goes down.
Complete data integrity
Cryptographic primitives ensure that data stored on the blockchain is immutable. Malicious actors cannot forge transactions or other data that has already been made public.
Getting Started With dApps on Ethereum
dApps are a new way of thinking about writing applications for the internet. Whether a user creates dApps or merely interacts with them, users will need to do sufficient research before getting started. Users will need to make use of a public and private key to start using any application on a blockchain network. In many cases, this ‘digital key’ is in place of a traditional username and password. dApp users will need to download a digital wallet (e.g. Metamask) and purchase some ETH (the currency used to pay for transaction fees on Ethereum). A wallet will allow users to connect to the network, and ETH will enable them to pay any transaction fees when using different dApps.
Exploring dApps
Many dApps are still in the early stages of development and are considered to be experimental in testing the possibilities of decentralized networks. However, many dApps have already seen significant market traction, with notable success in the financial, infrastructure, and gaming categories.
The finance sector has shown remarkable advancement in its services with the advent of blockchain technology. Since dApps use cryptocurrencies as the built-in medium of exchange, this could dramatically boost the mainstream adoption of cryptocurrencies by exposing more people to them. With all the hype in the DeFi (decentralized finance) space right now, DeFi applications (specifically decentralized exchanges, or DEXs) are among the first interactions individuals have with dApps.
Explore some of today’s dApp projects:
Why Businesses Should Care About dApps
dApps were specifically designed as an extension for interacting with various blockchains. Therefore, it comes as no surprise that dApps can be used for business purposes. While the opportunities of dApps may be more closely aligned with the benefits of the individual user, significant business potential persists. Forward-thinking companies are considering alternative digital assets on their balance sheet, resulting in a departure from more conventional investing. A good example of this is the partnership between Deutsche Telekom AG and Chainlink, where the telecommunications company is providing DeFi data support.
From a corporate perspective, global interest in blockchain technology and dApps has been around for some time. Back in 2018, PwC surveyed over 600 executives from 15 territories, with 84% saying that their organizations have at least some involvement with blockchain technology.
During 2018, in the wake of the hype of the 2017 explosion in cryptocurrency valuations, a tendency toward ‘blockchain tourism’ developed. Many intrigued companies explored the technology for a few weeks before deciding that they were more comfortable without it. However, as 2019 rolled around, we saw this trend fall away and companies began to place a greater focus on developing the technology as a means to solve persistent industry challenges. 2019 brought a greater diversification to the pool of blockchain players with more operating companies investing and allocating cash to digital assets and cryptocurrencies. The pool of potential customers is also growing. Fast forward to Q2 of 2020, and evidence shows that Ethereum doubled (97%) its amount of active dApp users with a sharp increase from 637,278 in the first quarter to 1,258,527 in Q2.
As dApps open up more doors for operating companies, businesses no longer need to ask, ‘will the technology work?’ but are instead focusing on the question, ‘how can the technology work for us?’
Blockchain networks like Ethereum remove the need for a third party to handle transactions between peers. This completely removes the need for a middle man, which is replaced by code. This saves companies significant costs and results in rapid business transactions. As the dApp ecosystem and the regulatory environment for digital assets continues to mature, exploring dApps is becoming more approachable to the mainstream.
A Non-Exhaustive List of dApp Benefits For Business
Business leaders are exploring how blockchain-based applications can help build more efficient processes and new financial models.
An alternative storage mechanism
Cloud storage is controlled by a few large providers (Google, Microsoft, etc.), which raises questions about data protection, privacy, control, and ownership of data. Instead of running storage through a company that controls it centrally, a decentralized blockchain network stores the data securely and privately.
Business intelligence and innovation
dApps enable new ways of organizing economic activities, reducing costs and time associated with intermediaries, and strengthening trust in an ecosystem of actors. Businesses exploring these types of disruptive technologies are often given pioneer status.
Decentralized control
A decentralized structure allows each party to run the app without having to trust any other party. This usually results in faster adoption of the application. Since dApps aren’t hosted on any particular IP address, there is less authority owning a dApp’s network and it is much more difficult for external authorities to prohibit a dApp.
Data integrity
Once information is added to the blockchain, it’s stored permanently, which means dApps are more resistant to modifications or restrictions.
Business transparency
dApp code is often open source, which means that it can be viewed by anyone who wants to verify the developers’ claims on what it does. While privacy laws and regulations differ from one country to the next, centralized applications still require users to input sensitive data.
Less downtime
dApps are more robust and flexible than centralized applications because they don’t require connectivity to a single centralized server to run. This means that enterprises can ensure minimal interruptions and downtime for maximum business continuity and resilience.
Cost reduction
dApps offer a higher transaction speed, which translates to cost reduction. Unlike centralized systems, organizations don’t need to install resource-heavy servers and hire experts to manage and maintain their servers and data.
Security
Unlike traditional single-server applications, dApps have no single point of failure which means that they are more resistant to attacks. A dApp will only fail if every single computer in the network fails which is near impossible.
Gartner forecasts that blockchain will generate an annual business value of more than US $3 trillion by 2030. It’s possible to imagine that 10% to 20% of global economic infrastructure will be running on blockchain-based systems by that same year.
dApps: Points of Consideration
While there are plenty of benefits of dApps, blockchain technology is still highly complex, meaning that developers, companies, and users have to understand and deal with transaction fees, wallets, security risks, and more.
Just as the internet facilitated the remote distribution of data, blockchain enables wide-scale decentralized exchanges. Clearly, there is potential here. But as with any new technology, key challenges need consideration first.
Inaccessibility
Onboarding native blockchain users into the dApp ecosystem is easy. However, it can be challenging to onboard non-blockchain, or Web2, users seamlessly into the space. In addition, given DeFi’s increasing popularity, some users are being priced out of the dApp ecosystem due to Ethereum's high network fees.
Lacking user experience
Since dApps don’t function in the same way that centralized applications do, the user experience is often more difficult to navigate. However, improved UX will come as more organizations turn to blockchain technology to make systems more efficient and less costly.
Security features
In the programming world, if there are errors deployed to your software, it will leave users and the platform susceptible to dangerous hacks. Traditional cybersecurity solutions won’t work which is why it is critical to use dApp-specific security solutions because they operate differently in a very distinct environment. While many companies with large development teams may be capable of handling an audit internally, it is advisable to use a competent third party to audit your codebase. This gives dApp users the added peace of mind that the application is proven to be secure, making it more appealing and less risky to use.
Protocol longevity
dApps can be built on different protocols, which is why developers need to account for longevity when choosing a blockchain. Is it still likely to be around in the next 5 to 10 years?
Network delays
At times, blockchain networks can become overwhelmed with the number of users participating and transacting on the network. This can affect the proper functioning of dApps, resulting in slow speed and payment processing time.
dApp interface
Many dApps are not yet mobile-native which means most of them have to be accessed on a desktop. However, we will see more dApps become mobile-native in the near future.
dApp development
Running a dApp in a complex programming environment makes application maintenance, debugging, and updates more challenging.
dApps: Remapping the Technological Landscape
While today’s dApps are merely scratching the surface in terms of their potential, we will see more use cases emerge as the technology matures. Currently, the core challenge in the path of blockchain’s large-scale adoption is stakeholder management and bringing competitors and collaborators together to solve shared problems.
As dApps continue to grow in number and more innovations enter the playing field, it is always important to understand the good and bad of each application. Governance will be critical, dApp audits will become a requirement, and data security will become of utmost importance. dApp ideas that can entice mass collaboration show significant promise to facilitate a new way for users to securely interact online and transact with novel financial systems and digital assets.
We are only beginning to experience what is possible with the development of the decentralized web. As more and more dApps are launched, we'll be one step closer to achieving a more democratized playing field of business participation and user value generation.
-------
This article does not provide any investment advice. All data is provided for information purposes only. No investment decision shall be based on the information provided here and you are solely responsible for your dApp research and investment decisions.




