Sustainable Food Systems: Why it is Time for a Responsible F&B Production

Eating and drinking are essential human needs. What once started with agriculture and animal husbandry has now evolved into a global food and beverage industry that has undergone significant changes and is facing various challenges. On one hand, there is a growing global population, with some individuals enjoying abundance while others suffer from hunger and urgently need healthy nutrition. On the other hand, our world is grappling with climate change and urgently requires responsible F&B production methods that prioritize animal welfare and environmental conservation. How can we achieve those goals while simultaneously minimizing our ecological footprint? In this article, we will delve into the environmental and societal impacts, explore avenues for improvement, and highlight innovative technological solutions for sustainable food systems.
Harnessing Opportunities for Responsible Food Production: Promoting Sustainability and Health
The global food and beverage (F&B) industry is at a crucial juncture, requiring immediate action to adopt responsible production methods that can effectively tackle a myriad of critical issues. From reducing food waste to promoting healthier choices and ensuring an efficient supply chain, there is an urgent need for transformation. This need aligns with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals, where “Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns” holds a prominent position as number 12. We have identified four key aspects that have a profound impact on both the environment and society. By addressing these aspects of sustainable food systems, companies can actively contribute to the security of supply and climate protection, as well as maintain competitiveness in the future.
Waste and Inefficiencies in the Supply Chain
Around 1.3 billion tonnes of food, equivalent to approximately 30 percent of global production, go to waste or remain unharvested every year. This would be enough to feed every hungry person twice.
Shockingly, 13.8 percent of this waste occurs during food production, including losses during harvesting, transportation, storage, and processing. The remaining waste occurs in households, food service establishments, and retail outlets.
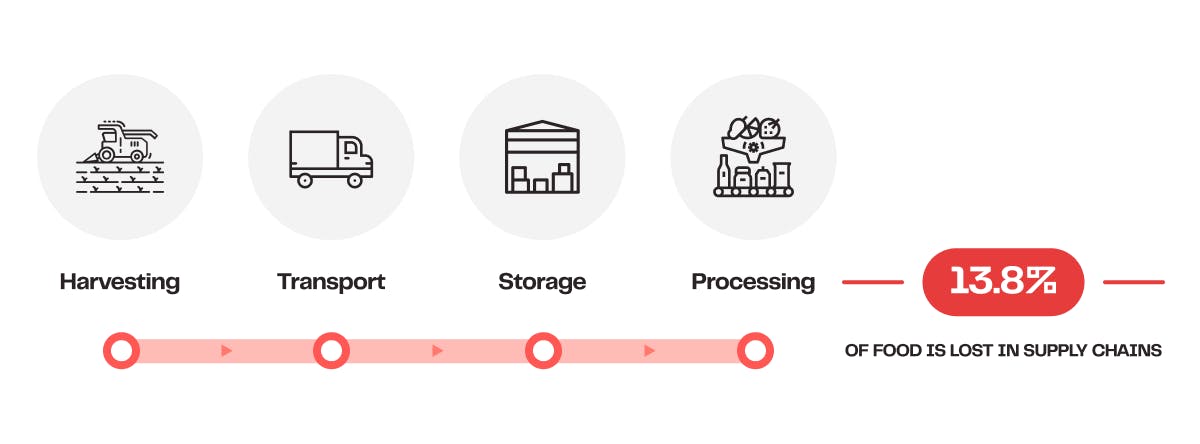
This staggering level of food waste not only leads to the destruction of nutritious food but also incurs a financial loss of over $400 billion annually. Moreover, its environmental impact is devastating. A study reveals that the global food supply accounts for approximately one-third of all greenhouse gas emissions. It is estimated that half of this is at the expense of food waste, as the rotting process in landfills as well as the waste infrastructure itself contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions.
Loss of Soil Fertility and Biodiversity
Unsustainable agricultural practices, characterized by excessive and indiscriminate use of chemical-intensive methods, directly contribute to the depletion of soil fertility and biodiversity. The overuse of synthetic chemicals disrupts the natural nutrient composition in the soil, leading to nutrient depletion, reduced soil quality, and increased vulnerability of crops to diseases and pests.
Additionally, the widespread adoption of monoculture farming, where large areas are dedicated to a single crop, disrupts natural ecosystems and reduces habitat diversity for native plants and animals. This disruption of the delicate ecological balance weakens agricultural systems’ resilience in the face of climate change and other environmental pressures.
Digital solutions can be a useful tool to address biodiversity loss and benefit local communities, if used wisely. Read more in out article IoT and the Battle Against Biodiversity LossBattle Against Biodiversity Loss.
To address these challenges, there is an urgent need for the industry to embrace organic farming methods. Practices such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and integrated pest management prioritize soil health and promote a more sustainable approach to agriculture. By implementing these sustainable practices, we can safeguard our food systems and ensure a healthier and more resilient future for generations to come.
Limited Access to Healthy and Nutritious Food
In the western world, we are fortunate to have easy access to a wide variety of foods, including fish, meat, vegetarian options, and even vegan choices. We can create or even order diverse meals using these ingredients, and if desired, opt for organic options. However, this privilege is not universal. In many parts of the world, food availability may not be scarce, but the quality and nutritional balance of the food are far from ideal. This has significant consequences, not only for public health but also for perpetuating social inequalities.
As mentioned earlier, it is astonishing to consider that the food we discard could potentially feed the world’s hungry population twice over. Unfortunately, our leftovers do not reach those in need. Consequently, many individuals are deprived of the opportunity to consume nutritious and sufficient meals. This disparity in access to healthy food further exacerbates the issue of food insecurity and widens the gap between different social groups.
Increasing Demand for Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Food
Consumer behavior in the realm of food has undergone a remarkable shift in recent years. More and more people are consciously opting out of consuming food items that have a negative impact on the environment or animal welfare.
This change signifies a heightened awareness of the wider implications of our dietary choices and emphasizes the escalating significance of responsible and sustainable practices within the food industry.
The future market will be challenging for products from factory farming, tropical fruits that are flown in when ripe, and unnecessary plastic packaging. The demand for these items is expected to decline. Instead, there will be a growing emphasis on regional and seasonal products of organic quality, as well as the popularity of markets and shops that offer packaging-free options. Consumers will prioritize sustainable and environmentally friendly choices, driving a shift towards more conscious and responsible purchasing habits. Meeting this demand poses a challenge for the industry, requiring a fundamental shift in production methods.
The Role of New Technologies in Sustainable Food Systems
As we can see, the global food system is at a critical point. In this context, the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies offers promising solutions for creating more sustainable food systems. Let’s examine how IoT and AI can contribute to sustainable food production, distribution, and consumption.
1 Monitoring and Optimization of Agricultural Practices
1.1 Precision Farming
IoT sensors and AI algorithms collect and analyze real-time data on soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health. Farmers can use this information to make data-driven decisions, optimizing irrigation, fertilization, and pest control. The result is increased crop yields and resource efficiency, reducing the environmental impact of agriculture.
For example, the Israeli tech company Taranis has developed an AI-powered image analysis system to detect crop diseases and pest infestations. Their platform also utilizes IoT sensors to monitor weed severity, disease, insect damage, and nutrient deficiencies, providing farmers with actionable insights to improve yield and reduce waste throughout the growing season and beyond.
Phytech is another company that develops a plant monitoring system using sensors to track plant growth and health. This allows growers to optimize irrigation, fertilization, and other inputs. The system consists of a small device attached to the plant, which measures plant tissue, temperature, and humidity to provide real-time data and insights.
1.2 Livestock Management
IoT devices equipped with sensors can monitor the health and well-being of livestock. AI algorithms process the data to identify early signs of illness or stress. By addressing these issues promptly, farmers can enhance animal welfare, reduce losses, and minimize the need for antibiotics, promoting both sustainability and ethical farming practices.
There are some remarkable solutions available on the market. Let’s highlight two examples: SenseHub a wearable sensor for livestock that monitors and tracks an animal’s temperature, activity level, and other vital signs to detect early signs of illness and disease. EggXYt addresses another challenge by using non-invasive genetic sensor technology to accurately identify the gender of chick embryos inside eggs before they hatch. This technology enables more efficient and ethical management of egg production and is expected to save the lives of billions of male chicks that are typically culled due to their inability to lay eggs nor being the fast-growing breeds that are sold as poultry.
1.3. Sustainable Agriculture and Aquaculture
IoT helps manage resources more efficiently. For example, in aquaculture, sensors can control the aeration systems in fish ponds, ensuring oxygen levels are optimal for fish without overusing energy. In agriculture, IoT-driven precision agriculture reduces the need for chemical inputs by targeting specific areas where they are required, minimizing waste.
Swiss based AgriCircle has developed an AI-based Precision Sampling method that revolutionizes soil analysis for improved soil vitality and crop yields. Unlike traditional modeling approaches, this method provides superior precision in determining carbon sequestration, making it a crucial factor in credible carbon offsets. By incorporating data-driven precision farming, AgriCircle considers the heterogeneity of soil properties in the field, allowing for precise and targeted management. This breakthrough enables the strategic buildup of carbon and soil nutrients in areas where they have the greatest impact, optimizing agricultural practices for enhanced sustainability and productivity.
2. Reduction of Food Waste
2.1 Supply Chain Optimization and Inventory Management
IoT technology provides real-time visibility into the movement of goods within the supply chain. Sensors track temperature, humidity, and other factors that affect food quality during transportation. AI algorithms can predict delays or spoilage, allowing for proactive adjustments. Inventory management also benefits from this technology: by analyzing data on consumer demand, expiration dates, and seasonal trends, retailers and food service providers can reduce overstocking and food waste, leading to cost savings and sustainability improvements, like the solutions of Winnow prove.
Learn more about sustainable supply chains in our article in our article.
2.2 Smart Kitchen Appliances
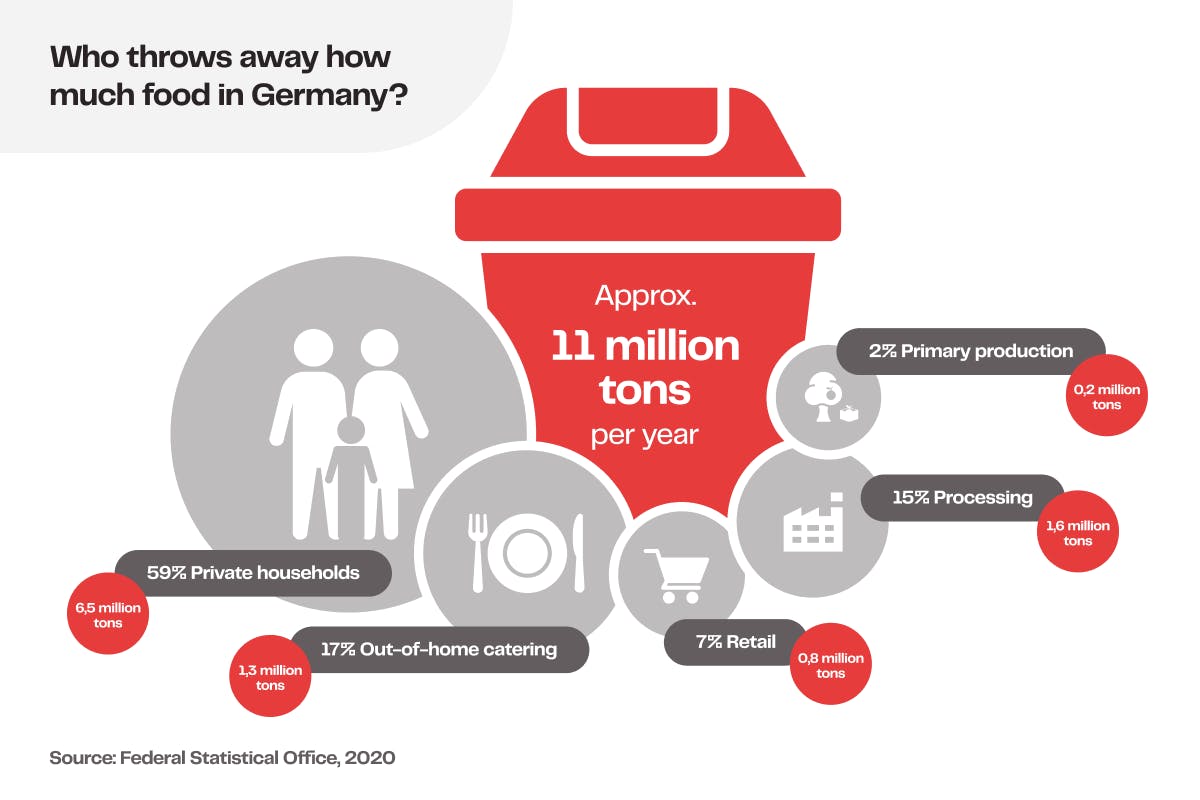
The majority of food waste occurs in households, with 60 percent of all food waste in Germany. While campaigns raise awareness about this excessive waste, another solution lies in smart kitchen appliances connected to the Internet of Things (IoT). These appliances, such as smart refrigerators and ovens, assist consumers in reducing food waste. By monitoring food inventory and suggesting recipes based on available ingredients, these devices promote more efficient use of groceries. For instance, if the refrigerator detects vegetables that are on the verge of spoiling, it can offer recipe suggestions that incorporate those ingredients.
3. Climate Change Mitigation
3.1 Climate-Resilient Farming
Climate-resistant agriculture refers to agricultural practices and technologies developed to minimize the impacts of climate change on food production. It encompasses water management, diversified crops and livestock, soil health, and early warning systems.
Transitioning to climate-resistant agriculture is crucial for sustaining food production in a changing environment and addressing the challenges of climate change.
Key aspects include adapting crop rotations, selecting resilient plant varieties, and implementing sustainable soil practices. Effective water management techniques such as efficient irrigation and rainwater collection, along with the use of drought-resistant plants, are essential. Establishing early warning systems for weather events helps farmers prepare for extreme weather. Overall, climate-resistant agriculture plays a vital role in maintaining food production and resilience in the face of climate change.
3.2 Carbon Footprint Reduction
The reduction of carbon footprints has become a top priority for industries worldwide, including the food sector. In this regard, the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies presents a significant opportunity for food producers and distributors to optimize energy usage and transportation routes, leading to a substantial decrease in carbon emissions and contributing to broader sustainability efforts. By embracing these innovative solutions, food producers and distributors actively participate in climate change mitigation initiatives and showcase their commitment to environmentally conscious practices.

IoT Reshaping F&B: Opportunities for Entrepreneurs
Implementing IoT technology has shown positive returns on investment (ROI) for businesses in the food and beverage industry. For instance, a study by Deloitte revealed that food manufacturing companies experienced a 20% reduction in operational costs and a 15% increase in production capacity after adopting IoT technology. Another study by IoT Analytics found that implementing IoT technology in supply chain management resulted in an average ROI of 15.6%.
The opportunities for entrepreneurs aiming to contribute to responsible F&B production through technology are thus immense. According to a report from MarketsandMarkets, the global IoT in the food and beverage market is projected to grow from $9.0 billion in 2020 to $35.5 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 31.4% during the forecast period. The precision farming market for example is expected to register a CAGR of 10.7% by 2025, which would make it a 21.9 billion-dollar industry.
This growth is driven by factors such as increased adoption of smart agriculture techniques, rising demand for processed foods as well as sustainable food, and the need for real-time data analytics.
Transforming Beverage Production: Founders Tap into NBT's Power for Innovation
Two founders who discovered the potential for themselves are using the power of NBT as a venture studio to further develop their idea. With their AIoT plug and play solution, Nikhil Ninne and Dr. Konstantin Bellut are revolutionizing the beer brewing process. By monitoring and visualizing the mashing and fermentation processes in real time, brewers can make data-based decisions instead of having to rely on extensive samples. The result: time savings of 850 man-hours per year and consistent quality, as sampling-related contaminations and analysis errors can be reduced by 90%. The solution is also good for the environment: energy consumption can be reduced by 1.5% through reduced fermenter cooling alone, plus an increase in CO2 recovery of over 10%.
"The global beer industry is more than six times bigger than the milk industry. The market is hotly contested. Cost pressures are increasing, both in terms of gas and electricity costs, as well as ingredients and packaging materials," says Nikhil. Konstantin continues, "In addition, there are a lot of new beer brands and the pressure to produce more high quality complex products. We are convinced that we can provide the beer industry with a suitable solution so that they can hold their own in this challenging market environment and even position themselves as pioneers."
Creating a sustainable future requires responsible F&B production in order to cultivate a food industry that prioritizes the well-being of both people and the environment. NBT venture studio offers founders the opportunity to collaborate and receive the necessary support and expertise to build tech businesses that contribute to sustainable and responsible F&B production. Reach out to us to discover the possibilities of collaboration and make a positive impact togethermake a positive impact together!




